Quite a while back, one could open the keyboard viewer from the menu bar, choose a font, and see what characters were in it.
There must be something similar now, but the emoji, symbols, & keyboard viewers are rather simplistic. In Pages, there's no other way that I know of to find a character that isn't in any of those, such as the symbol for the Command key.
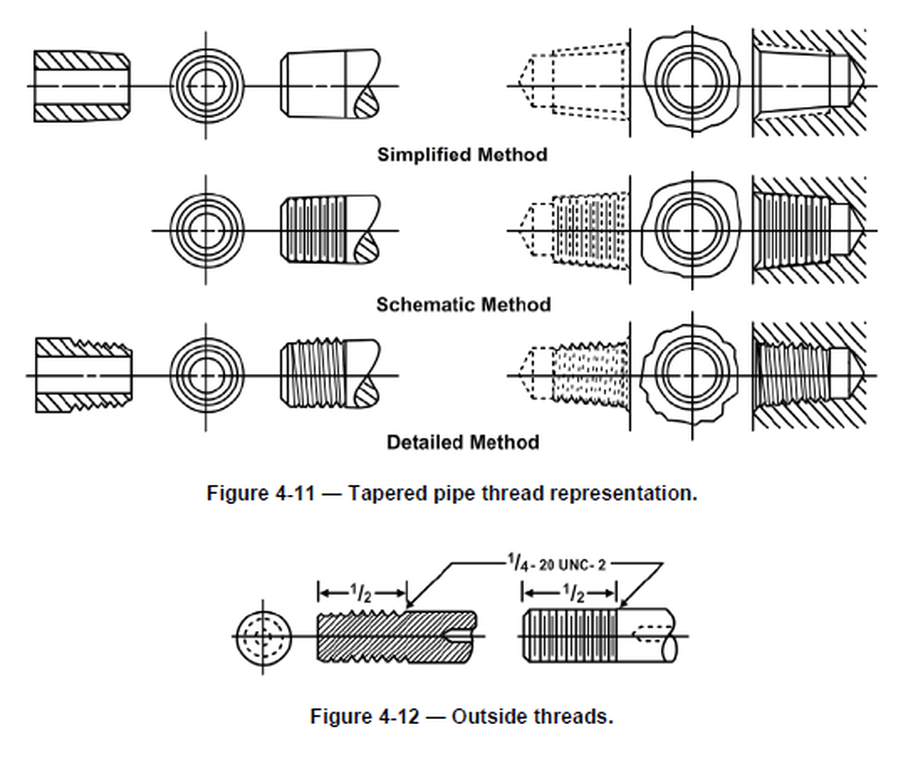
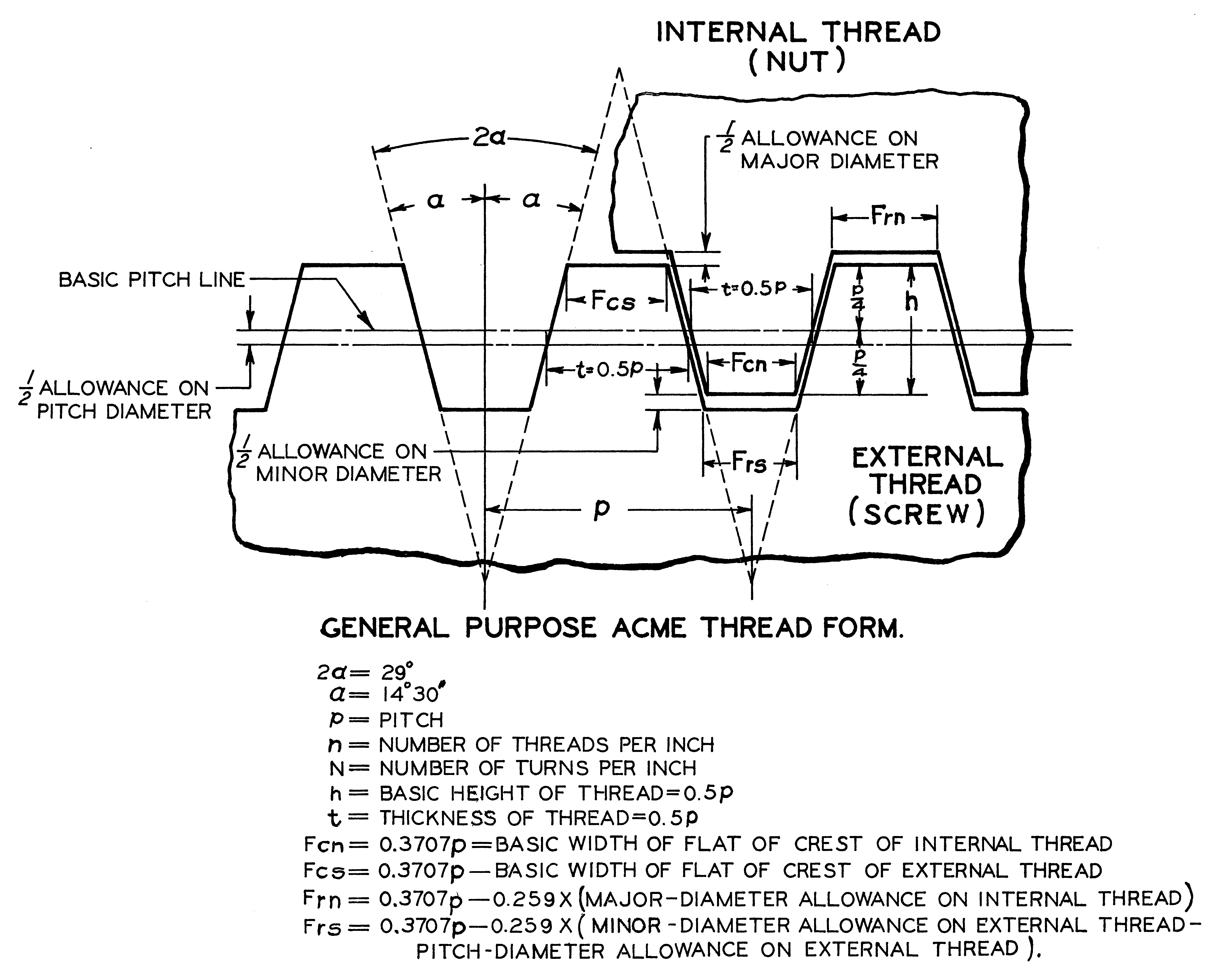
Symbol: Category: Feature of Size Definition: Least material condition is a feature of size symbol that describes a dimensional or size condition where the least amount of material (volume/size) exists within its dimensional tolerance. The callout also overrides GD&T Rule#2 or the Regardless of Feature Size rule. For external threads, two classes of tolerances on the pitch diameter are specified; these are Class A and Class B. The choice between class A and class B depends on the conditions of application. The symbol for pipe thread type is G for external and internal threads.
If I open one of the Adobe apps, I can use the Glyphs to get it, but there has to be some way to do it in Apple apps. 4 you clothing.
Help!
Thanks.
Mac Pro, OS X El Capitan (10.11.6)
Posted on Aug 30, 2017 12:54 PM
Our Comprehensive List of GD&T Symbols.
We conveniently grouped the GD&T Symbols into various categories according to when each is used in. Be sure to click on the links to get more information on each GD&T symbol or concept. We will be adding to this list periodically as we continue to build up our content.
Position is one of the most useful and most complex of all the symbols in GD&T. The two methods of using Position discussed on this page will be RFS or Regardless of Feature Size and under a material condition (Maximum Material Condition or Least Material Condition). Position is always used with a feature of size.
Symbol: None – Always Implied default condition (abbreviated: RFS) Category: Feature of Size Definition: Regardless of Feature Size (RFS) is the default condition of all geometric tolerances by rule #2 of GD&T and requires no callout. Regardless of feature size simply means that whatever GD&T callout you make, is controlled independently of the size dimension of the part. This..
Thread Type Symbol Crossword
Symbol: Category: Feature of Size Definition: Least material condition is a feature of size symbol that describes a dimensional or size condition where the least amount of material (volume/size) exists within its dimensional tolerance. The callout also overrides GD&T Rule#2 or the Regardless of Feature Size rule. For simplicity: If it is a hole or internal feature: LMC..
Symbol: Category: Feature of Size Definition: Maximum Material Condition or for short, MMC, is a feature of size symbol that describes the condition of a feature or part where the maximum amount of material (volume/size) exists within its dimensional tolerance. The callout also removes GD&T Rule#2 which states that all geometry tolerances are controlled independently..

Thread Type Symbol Chart
Symbol: Definition: A datum is theoretical exact plane, axis or point location that GD&T or dimensional tolerances are referenced to. You can think of them as an anchor for the entire part; where the other features are referenced from. A datum feature is usually an important functional feature that needs to be controlled during measurement as..
Help!
Thanks.
Mac Pro, OS X El Capitan (10.11.6)
Posted on Aug 30, 2017 12:54 PM
Our Comprehensive List of GD&T Symbols.
We conveniently grouped the GD&T Symbols into various categories according to when each is used in. Be sure to click on the links to get more information on each GD&T symbol or concept. We will be adding to this list periodically as we continue to build up our content.
Position is one of the most useful and most complex of all the symbols in GD&T. The two methods of using Position discussed on this page will be RFS or Regardless of Feature Size and under a material condition (Maximum Material Condition or Least Material Condition). Position is always used with a feature of size.
Symbol: None – Always Implied default condition (abbreviated: RFS) Category: Feature of Size Definition: Regardless of Feature Size (RFS) is the default condition of all geometric tolerances by rule #2 of GD&T and requires no callout. Regardless of feature size simply means that whatever GD&T callout you make, is controlled independently of the size dimension of the part. This..
Thread Type Symbol Crossword
Symbol: Category: Feature of Size Definition: Least material condition is a feature of size symbol that describes a dimensional or size condition where the least amount of material (volume/size) exists within its dimensional tolerance. The callout also overrides GD&T Rule#2 or the Regardless of Feature Size rule. For simplicity: If it is a hole or internal feature: LMC..
Symbol: Category: Feature of Size Definition: Maximum Material Condition or for short, MMC, is a feature of size symbol that describes the condition of a feature or part where the maximum amount of material (volume/size) exists within its dimensional tolerance. The callout also removes GD&T Rule#2 which states that all geometry tolerances are controlled independently..
Thread Type Symbol Chart
Symbol: Definition: A datum is theoretical exact plane, axis or point location that GD&T or dimensional tolerances are referenced to. You can think of them as an anchor for the entire part; where the other features are referenced from. A datum feature is usually an important functional feature that needs to be controlled during measurement as..
Special Note: Perpendicularity in GD&T can mean two very different things depending on which reference feature is called out. The normal form or Surface Perpendicularity is a tolerance that controls Perpendicularity between two 90° surfaces, or features. Surface Perpendicularity is controlled with two parallel planes acting as its tolerance zone. Axis Perpendicularity is a tolerance..
GD&T Symbol: Relative to Datum: Yes MMC or LMC applicable: No Drawing Callout: Description: Total Runout is how much one entire feature or surface varies with respect to a datum when the part is rotated 360° around the datum axis. Total runout controls both the amount of variation in the surface as the part is..
GD&T Flatness is a common symbol that references how flat a surface is regardless of any other datum's or features. It comes in useful if a feature is to be defined on a drawing that needs to be uniformly flat without tightening any other dimensions on the drawing. The flatness tolerance references two parallel planes (parallel to the surface that it is called out on) that define a zone where the entire reference surface must lie.
GD&T Symbol: Relative to Datum: Yes MMC or LMC applicable: No Drawing Callout: Description: GD&T Symmetry is a 3-Dimensional tolerance that is used to ensure that two features on a part are uniform across a datum plane. An established 'true' central plane is established from the datum and for the symmetry to be in tolerance,..
Special Note: Straightness actually has two very different functions in GD&T depending on how it is called out. In its normal form or Surface Straightness, is a tolerance that controls the form of a line somewhere on the surface or the feature. Axis Straightness is a tolerance that controls how much curve is allowed in..
GD&T Symbol: Relative to Datum: Yes MMC or LMC applicable: Yes (Uncommon) Drawing Callout: Description: Angularity is the symbol that describes the specific orientation of one feature to another at a referenced angle. It can reference a 2D line referenced to another 2D element, but more commonly it relates the orientation of one surface plane..
Example Frame: Definition: In GD&T, a feature control frame is required to describe the conditions and tolerances of a geometric control on a part's feature. The feature control frame consists of four pieces of information: GD&T symbol or control symbol Tolerance zone type and dimensions Tolerance zone modifiers: features of size, projections… Datum references (if..
GD&T Symbol: Relative to Datum: Yes MMC or LMC applicable: No Drawing Callout: Description: Concentricity, sometimes called coaxially, is a tolerance that controls the central axis of the referenced feature, to a datum axis. The axes for the datum and referenced feature are derived from the median points of the part or feature. Concentricity is..
GD&T Symbol: Relative to Datum: Yes MMC or LMC applicable: No Drawing Callout: Description: Runout is how much one given reference feature or features vary with respect to another datum when the part is rotated 360° around the datum axis. It is essentially a control of a circular feature, and how much variation it has..
GD&T Symbol: Relative to Datum: Optional MMC or LMC applicable: No Drawing Callout: Description: Profile of a surface describes a 3-Dimensional tolerance zone around a surface, usually which is an advanced curve or shape. If it is called out on a curved surface, like a fillet on a welded part, the entire surface where the..
GD&T Symbol: Relative to Datum: No MMC or LMC applicable: No Drawing Callout: Description: The Cylindricity symbol is used to describe how close an object conforms to a true cylinder. Cylindricity is a 3-Dimensional tolerance that controls the overall form of a cylindrical feature to ensure that it is round enough and straight enough along..
GD&T Symbol: Relative to Datum: No MMC or LMC applicable: No Drawing Callout: Description: The circularity symbol is used to describe how close an object should be to a true circle. Ca casinos closed. Sometimes called roundness, circularity is a 2-Dimensional tolerance that controls the overall form of a circle ensuring it is not too oblong, square, or..
GD&T Symbol: Relative to Datum: Optional MMC or LMC applicable: No Drawing Callout: Description: Profile of a line describes a tolerance zone around any line in any feature, usually of a curved shape. Profile of a line is a 2-Dimensional tolerance range that can be applied to any linear tolerance. If it is called out..
Thread Symbols In Engineering Drawing
Special Note: Parallelism actually has two different functions in GD&T depending which reference feature is called out. The normal form or Surface Parallelism is a tolerance that controls parallelism between two surfaces or features. The surface form is controlled similar to flatness with two parallel planes acting as its tolerance zone. Axis Parallelism is a tolerance..
